Six Sigma
The principle of Six Sigma is to eliminate deep systemic problems caused by variations in process.
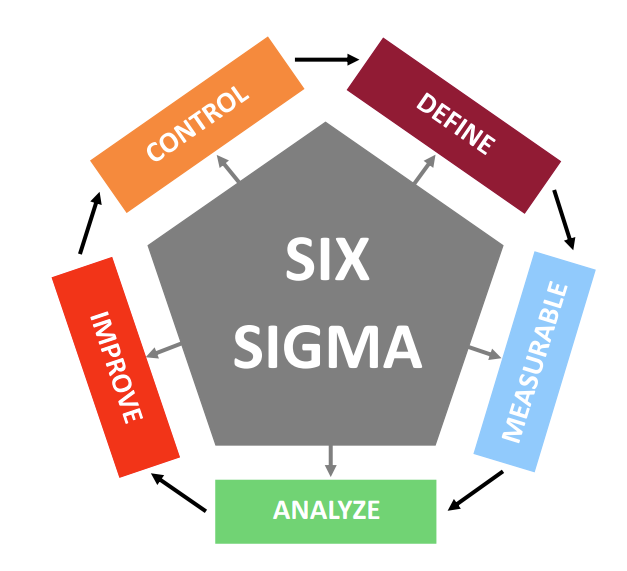
DMAIC Methodology
A core Six Sigma methodology focused on continuous process improvement. DMAIC provides a structured, data-driven approach to identify problems, measure performance, analyze root causes, implement effective solutions, and maintain long-term control. It helps organizations reduce variation, eliminate defects, and enhance overall efficiency and quality.
Define SMART statement
The first phase of DMAIC focuses on clearly identifying the problem and setting a direction for improvement. It involves creating a SMART statement to establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals. During this phase, the team works to understand the problem in detail, define the project’s objectives, assess the impact of the current situation, and ensure alignment with the voice of the customer (VOC). A hypothesis statement is also developed to guide further investigation and analysis.
Measurement system analysis
The Measure phase focuses on collecting accurate data to understand the current process performance. Before moving to the Analysis phase, it’s essential to ensure the reliability of all measurement systems. This involves auditing existing measurement tools, verifying gauge reliability, and confirming repeatability and reproducibility (R&R). The goal is to establish a solid data foundation that accurately reflects process capability and its ability to meet the voice of the customer (VOC).
Analyze (statistical tools, process capability-Cpk)
The Analyze phase focuses on discovering the root causes of process variation and validating the project’s hypothesis. This stage involves identifying and understanding critical inputs (Xs) that significantly impact the outputs (Ys) and overall process performance. Teams study the process flow, explore variables influencing the voice of the customer (VOC), and establish clear X–Y correlations. Through data-driven analysis, the true sources of inefficiency or defects are revealed, setting the foundation for targeted improvements.
Improve (faster, cheaper)
The Improve phase focuses on developing, testing, and implementing effective solutions to address the root causes identified in the Analyze phase. Teams pilot improvement changes to evaluate their effectiveness and validate results before full-scale implementation. This phase also includes establishing provisional standards to guide the new process and confirming the impact of critical Xs on performance. The goal is to ensure that improvements are both sustainable and deliver measurable benefits to the process and the customer.
Control (documented and maintained)
The Control phase ensures that the improvements achieved are sustained over time. This involves implementing permanent standards to maintain consistency in the improved process and prevent regression. An audit system is established to regularly monitor performance and ensure compliance with the new standards. Additionally, a look-across plan is developed to identify opportunities for applying successful improvements to other areas or processes within the organization, promoting continuous improvement across the business.
Training and Certification
Kenkyona offers comprehensive Six Sigma training and certification programs designed to equip individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to lead successful improvement projects. Our training covers all aspects of the DMAIC methodology, statistical tools, and practical applications of Six Sigma principles. Participants can earn Yellow Belt, Green Belt, or Black Belt certifications. We also offer virtual training options for Green and Black Belts to accommodate diverse learning needs.